What is Sustainability?
Definition
We define sustainability as the practice of promoting social, economic, and environmental well-being for all members of the community in a way that recognizes and addresses systemic inequalities and discrimination.
Sustainability consists of three elements, sometimes referred to as the "Three E's":
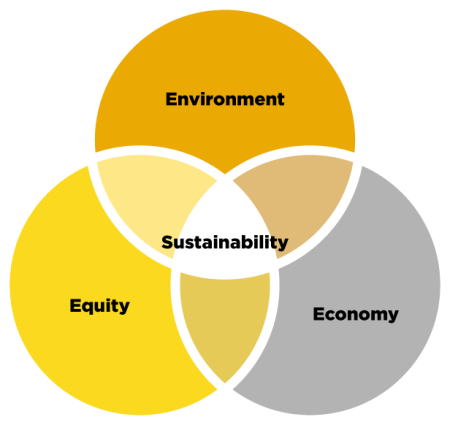
Environment
Protecting and preserving the natural resources upon which all life on Earth depends.
Equity
Centering social justice and climate justice so that historically marginalized communities and communities of color do not disproportionately bear environmental and economic burdens.
Economy
Promoting an economic system that can produce the goods and services necessary for our way of life while also preserving non-renewable resources and ensuring workers' rights and wellbeing.
Sustainable solutions must include all of these dimensions.
Consideration of the future is also a key element of sustainability. The basic idea behind sustainability is that the current generation can meet its needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs (Brundtland Report, 1987). There are other considerations depending on the perspective of the person defining the term. For example, economists will include an element that addresses the efficient allocation of scarce resources with intergenerational considerations while an ecologist would frame the discussion in terms of temporal ecosystem functions, biodiversity, or resiliency. Regardless of the discipline, all decisions made around the world today should consider how to implement sustainability in practice.