Energy & Buildings
Our energy efficiency program is CSULB’s longest running sustainability initiative. Since the mid 70’s the campus has made steady progress to improve energy efficiency and reduce campus utility costs from electricity and natural gas. Since 1974, a range of energy efficiency projects have been implemented which have collectively reduced the overall energy intensity (the amount of energy use per square foot of space) of campus buildings by more than 50%. Today, we remain committed to reducing the energy consumption of existing buildings through on-going retrofit projects and shrinking the energy and carbon footprint of new buildings through energy efficient sustainable design.
Energy best practices that CSULB currently undertakes in new and existing buildings:
- LED lighting with occupancy controls
- Energy efficient demand based heating and air conditioning (HVAC) systems
- High performance building envelope systems such as Low-e windows and cool white roofs
- Energy meters with real-time dashboard monitoring software
- Retro-commissioning of energy consuming systems in existing building
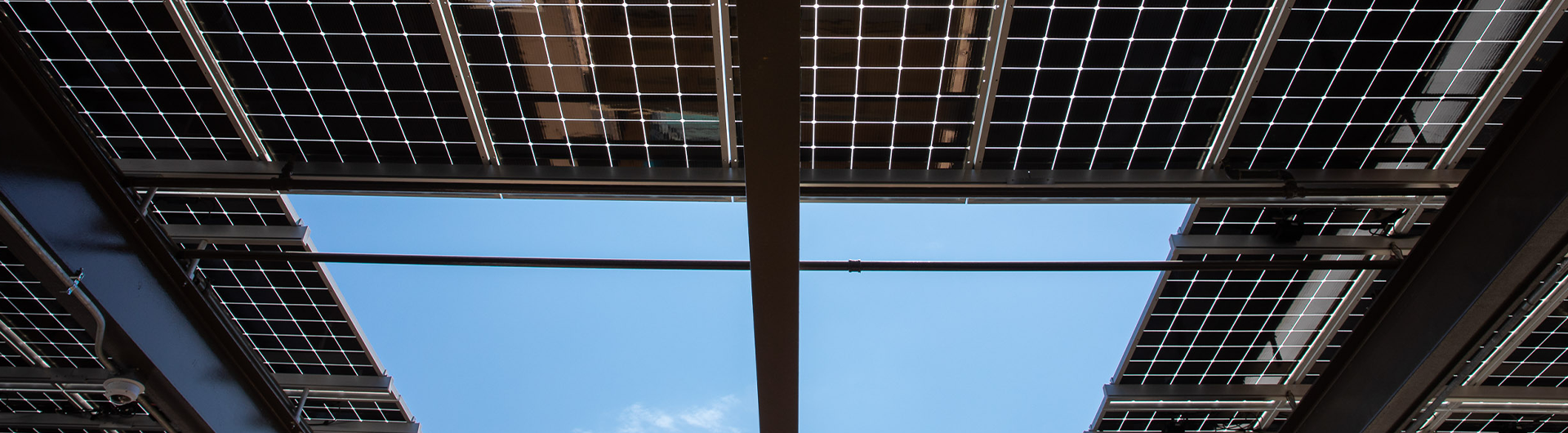
The campus has six solar power systems which account for approximately 15% of campus peak electrical load. The smaller photovoltaic systems are located on the roofs of Brotman Hall and the Vivian Engineering Complex and a carport in the Facilities Management. The largest solar power system on campus is the 4.75 megawatt system that is co-located in the general parking lots (G6, G7 & G8) on the north side of campus and in the employee parking lot (E8) on the south end of campus. When it came online in 2018, this system was the largest solar array on any of the 23 CSU campuses and the largest in the entire city of Long Beach.
CSULB is committed to increasing the amount of solar power generated on campus and encouraging our utility provider to source more electricity from renewable sources and take steps to phase out the dirtiest fuel sources from its energy mix.
Currently, CSULB’s main sources of energy are natural gas and electricity purchased from external utility providers. Natural gas is the primary energy source used to heat campus buildings, and although it is a fossil-based fuel source, it is generally considered a cleaner energy source when compared to other non-renewable sources such as coal.
Electricity, which is generated using a mix of energy sources, is the largest campus utility cost and the second largest source of campus greenhouse gas emissions. To achieve our goal of climate neutrality as outlined in the Climate Action and Adaptation Plan, CSULB must reduce the consumption of electricity by continuing to implement energy efficiency measures while also increasing the share of energy we consume that comes from renewable sources.
CSU policy mandates that all new buildings and major renovations meet or exceed the minimum requirements equivalent to the US Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Silver Level building standard. The LEED system provides guidelines on green building practices, materials and technologies that conserve energy and water and create healthy spaces that are conducive to working and learning.
In addition to adhering to LEED green building standards, CSULB is committed to pursuing the principles of Net Zero Energy to all new campus buildings. These buildings will be designed to not only minimize consumption of energy and other natural resources, but also to use only as much energy as they can generate from renewable energy sources such as solar photovoltaic systems.
CSULB is committed to maintaining clean, healthy, and safe buildings for our students, faculty, and staff while simultaneously minimizing negative impacts on the natural environment.
For this reason, the Facilities Management Department, which provides custodial services to the majority of the buildings on campus*, has adopted a Green Cleaning Policy and High Performance Cleaning Program to ensure that our cleaning processes, procedures and products:
- Contribute to better indoor air quality
- Minimize worker and building occupants’ exposure to potentially harmful or irritating chemicals
- Minimize emissions of climate altering and ozone depleting chemicals
- Require less water and create less waste
Examples of the Green Cleaning Policy and High Performance Cleaning Program in action include the use of:
- Green Seal certified, environmentally friendly cleaning products for routine cleaning
- Concentrated cleaning products to reduce packaging waste and environmental impacts of shipping
- Cleaning equipment (such as vacuums and floor polishers) that use less water, energy, and chemicals and produce less emissions
- Non-paper based hand drying systems
*The University Student Union, Student Recreation & Wellness Center, Residence halls, Beach Shops dining facilities, athletic facilities, and Foundation buildings are serviced by their own custodial service programs