Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
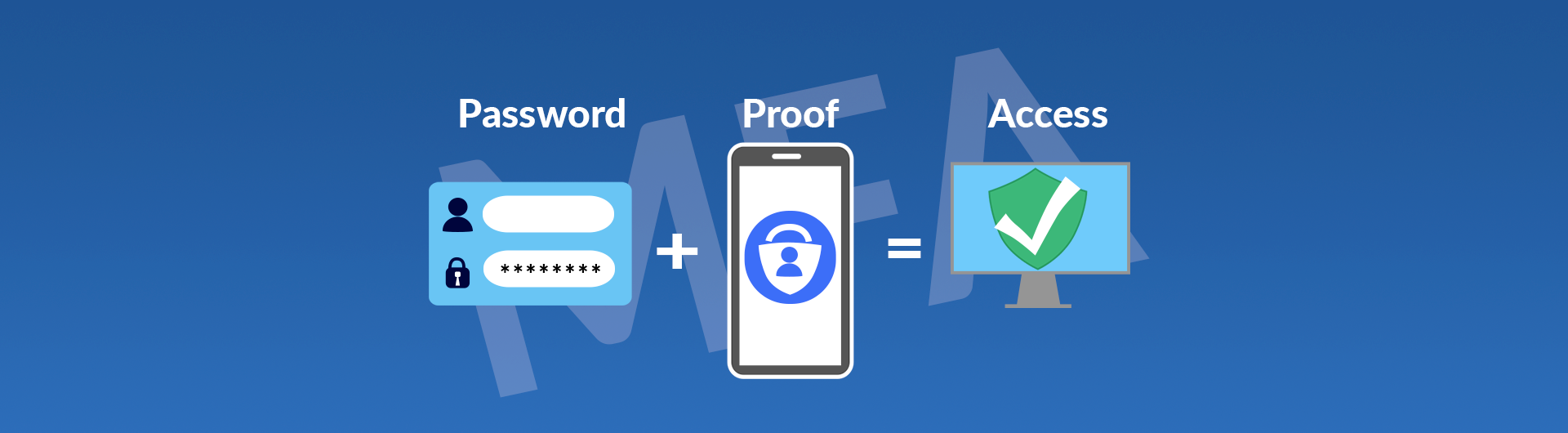
With MFA protection, if your password is compromised, an attacker will have an additional barrier preventing access. MFA is a security layer that requires a two-step verification process. The two verification methods typically required to prove your identity are 1) information you know - your username - and password AND 2) a unique item you have - typically your cell phone.
You may already be using MFA to protect access to online services like your bank, Gmail or Facebook accounts.
MFA does not stop all types of attacks and does not guarantee security, but it does add an additional level of authentication that reduces the risk of compromises by making cyberattacks more difficult.
How MFA Helps Our University
Data breaches and device compromises are widespread in today’s ever-connected world of remote work and instruction. Our campus community is vulnerable to these threats. It can be a challenge to recognize the difference between a legitimate login screen and one that’s set up as a phishing scheme to capture your username and password for use in fraudulent schemes or criminal activity.
Background
A CSU campus suffered a ransomware attack in 2020. As a preventative measure to cyberattacks, the Chancellor’s Office urged all CSU campuses to implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), also known as two-step verification, for all students and employees. Approximately 1,000 CSULB employees with access to sensitive CFS information or that manage information systems and services were the very first users of MFA. The use of MFA was expanded to all students on January 27, 2021 and to the rest of employees (including student assistants and volunteers) on February 24, 2021.