What is research?

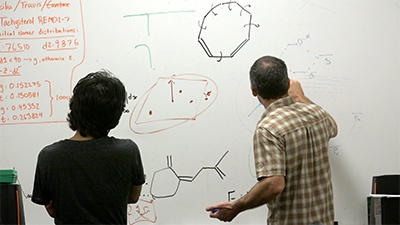
When many people hear the term “research” they immediately think of laboratories filled with Bunsen burners, test tubes, and Erlenmeyer flasks. However, not all research takes place in the lab or involves chemical reactions.
Research typically starts with a hypothesis, which is a testable, proposed explanation for a phenomenon. From that starting point, researchers design experiments that will either support or refute the hypothesis or parts of it. Other types of research are more preliminary in nature, focused on generating rather than testing hypotheses. This type of research may be guided by “research questions” rather than a hypothesis.
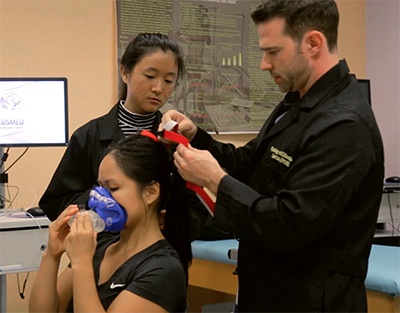
Research can be classified as Quantitative or Qualitative and as Basic or Applied. It can be conducted in the field or in the lab and can involve chemicals, living organisms or human subjects. Sometimes, research is even conducted virtually using computer models.
Quantitative Research
At the heart of quantitative research is measurement. Research is considered quantitative if it is observational or experimental in nature and results in numbers—data—that can be compared to past results or to project possible future results.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has no hard and fast numbers. It analyzes subjective data, such as what people do and say. It is exploratory and open-ended. Qualitative research deals with characteristics, symbols, definitions, metaphors, and descriptions of things, rather than measurable data.


Basic Research
Basic research seeks to contribute to overall scientific knowledge. Sometimes it is referred to as fundamental research because it informs the foundations of a subject area. It often does not produce results that are of immediate practical or commercial value.
Applied Research
Applied research seeks to solve practical problems in the real world. It often uses the results of basic research to create solutions to real-world problems.
Natural vs. Behavioral Sciences
Research can be conducted in a variety of disciplines. Sciences that tend to use quantitative data to explore the natural world are sometimes referred to as the “natural” or “hard” sciences and include biology, chemistry, physics, and others.
Sciences that tend to use qualitative data to study human and animal behavior, are often referred to as the “behavioral” or “soft” sciences and include psychology, sociology, anthropology, and others.
Many scientific disciplines use both quantitative and qualitative research.